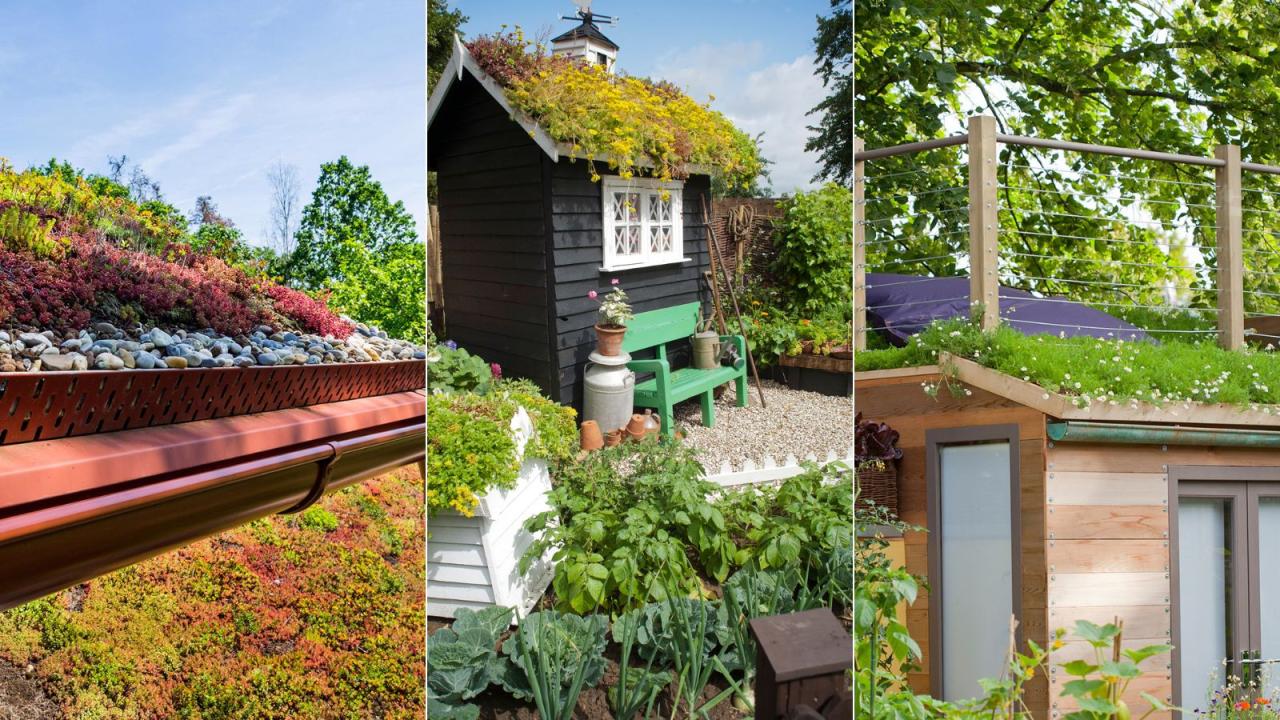
Green roofs add visual interest and provide a replacement habitat for the wildlife which was displaced when the building was erected. They provide heat insulation in winter, cooling in the summer and efficient sound insulation. Growing plants improve the air quality by reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, thereby helping to combat global warming. Green roofs slow the rate of rainwater run-off following heavy downpours, thus reducing the risk of flash flooding.
Vital Questions to Consider Before Making a Green Roof
Garages, sheds, log-cabins, playhouses and summerhouses can all be given the green roof treatment. At the outset two vital questions must be considered; these are: can the building support the load of a saturated green roof and will the roof be waterproof? When garages and house extensions are involved it pays to consult a structural engineer.
The Different Types of Roof Garden
- Traditional or intensive roof gardens are comprised of lawns, planting beds, paving and water features. Although attractiive, provided they are regularly maintained, they do require substantial structural support which adds considerably to building costs. Construction is not a job for the D.I.Y enthusiast.
- Green or extensive roofs cost little more than standard roofs to construct. They consist of lightweight layers of waterproofing, drainage material and 10cm of growing medium. Plants used, for instance, must be tolerant of extreme conditions of temperature, wind and drought.
- Semi-extensive roof gardens use the same lightweight materials and layers as the extensive system but employ a slightly greater depth of growing medium This increases the loading on the roof, but enables a more interesting range of plants to be grown including Ajuga, Ferns Nepeta, Origanum and Salvia.
How to Make an Extensive Roof Garden
The lightest and simplest form of green roof can be purchased ready grown. Sedum species are grown on rolls of special geo-textile matting. A root barrier such as heavy duty polythene or a pond liner should be laid on top of the existing roof. This is followed by a moisture retention mat which helps make sure the plants have the right amount of air and water to stay healthy. Batons are screwed on the outside edge of the roof before matting is rolled out and cut to fit inside the batons.
How to Make a Semi-extensive Roof Garden
As with the extensive system a pond liner is laid on the roof followed by a moisture blanket. A simple wooden framework made from preservative treated wooden planks up to 20cm deep and divided into 60cm square sections is placed over the roof, but doesn’t rest directly on it. Instead it is fastened to stout vertical posts which are concreted into the ground along the sides and corners of the building.The frame is filled with a light free draining mix containing 80% crushed brick rubble, peat substiture and perlite plus 20% John Innes Compost No 3. Plug plants are planted into this mix.
Shout the Virtues of This Type of Gardening From the Rooftops
Maintenance of green roofs is minimal, usually a couple of checks annually to remove weeds resulting from weed blown seeds. Once established there is no need to water or feed the plants. That previously utilitarian building becomes a living, growing, much talked about focal point.